Solution Or Across A Semipermeable Membrane. Simple Diffusion Is Carried Out By The Actions Of Hydrogen Bonds Forming Between Water Molecules An / Transport Across Membranes Boundless Anatomy And Physiology : This tubing allows small molecules (e.g., water, ions, glucose) to pass while preventing large molecules (e.g., macromolecules like proteins, starch, glycogen) from moving across.
Solution Or Across A Semipermeable Membrane. Simple Diffusion Is Carried Out By The Actions Of Hydrogen Bonds Forming Between Water Molecules An / Transport Across Membranes Boundless Anatomy And Physiology : This tubing allows small molecules (e.g., water, ions, glucose) to pass while preventing large molecules (e.g., macromolecules like proteins, starch, glycogen) from moving across.. Imagine a beaker with a semipermeable membrane separating the two sides or halves. An obvious question is what makes water move at all? Simple diffusion is carried out by the actions of hydrogen bonds forming between water molecules an : Water molecules move in to surround individual solute molecules. The rate of simple diffusion is affected by properties of the cell, the size of diffusing.
Solution or across a semipermeable membrane. Solution or across a semipermeable membrane. Simple diffusion is the process by which solutes are moved along a concentration gradient in a solution or across a semipermeable membrane.simple diffusion is carried out by the actions of hydrogen bonds forming between water molecules and solutes. Simple diffusion is carried out by the actions of hydrogen bonds forming between water molecules and solutes. 윤서인 백남기 / ë‚⃜를 ìžšì§€ë§ ì•„ìš ìœ¤ì„œì ¸ 백남기 ì¡°ë.
Osmosis is the diffusion of water molecules across a semipermeable membrane from an area of lower concentration solution (i.e., higher concentration of water) to an area of higher concentration solution (i.e., lower concentration of water).
Water molecules move in to surround individual solute molecules. Simple diffusion is carried out by the actions of hydrogen bonds forming between water molecules an / simple diffusion vs. An obvious question is what makes water move at all? Ch103 chapter 8 homeostasis and cellular function chemistry / the diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane is called osmosis. Imagine a beaker with a semipermeable membrane separating the two sides or halves. Hydrogen ions, or protons, will diffuse from an area of high proton concentration to an area of lower proton concentration, and an electrochemical concentration gradient of protons across a membrane can be harnessed to make atp. Due to the relatively high water permeability of some epithelial cells, it was long suspected that some additional mechanism for water transport across membranes must. Simple diffusion is the process by which solutes are moved along a concentration gradient in a solution or across a semipermeable membrane.simple diffusion is carried out by the actions of hydrogen bonds forming between water molecules and solutes. Simple diffusion is carried out by the actions of hydrogen bonds forming between water molecules an : Osmosis transports only water across a membrane. Water moves into and out of cells by osmosis. The mechanism of facilitated water transport and the probable existence of water pores has attracted researchers since 1957. Solution or across a semipermeable membrane.
Proteins can change shape when their hydrogen bonds are affected, but this may not fully explain this mechanism. Simple diffusion is the process by which solutes are moved along a concentration gradient in a solution or across a semipermeable membrane. Hydrogen ions, or protons, will diffuse from an area of high proton concentration to an area of lower proton concentration, and an electrochemical concentration gradient of protons across a membrane can be harnessed to make atp. Ch103 chapter 8 homeostasis and cellular function chemistry / the diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane is called osmosis. Water, like other substances, moves from an area of high concentration to one of low concentration.

The process by which solutes are moved along a concentration gradient in a solution or across a semipermeable membrane.
Osmosis is a special case of diffusion. This tubing allows small molecules (e.g., water, ions, glucose) to pass while preventing large molecules (e.g., macromolecules like proteins, starch, glycogen) from moving across. Due to the relatively high water permeability of some epithelial cells, it was long suspected that some additional mechanism for water transport across membranes must. Simple diffusion is carried out by the actions of hydrogen bonds forming between water molecules an : Simple diffusion is the process by which solutes are moved along a concentration gradient in a solution or across a semipermeable membrane. Simple diffusion is carried out by the actions of hydrogen bonds forming between water molecules an / simple diffusion vs. Imagine a beaker with a semipermeable membrane separating the two sides or halves. Solution or across a semipermeable membrane. 윤서인 백남기 / ë‚⃜를 ìžšì§€ë§ ì•„ìš ìœ¤ì„œì ¸ 백남기 ì¡°ë. Proteins can change shape when their hydrogen bonds are affected, but this may not fully explain this mechanism. Water moves into and out of cells by osmosis. Simple diffusion is the process by which solutes are moved along a concentration gradient in a solution or across a semipermeable membrane.simple diffusion is carried out by the actions of hydrogen bonds forming between water molecules and solutes. Simple diffusion is carried out by the actions of hydrogen bonds forming between water molecules an :
Water molecules move in to surround individual solute molecules. Simple diffusion is the process by which solutes are moved along a concentration gradient in a solution or across a semipermeable membrane.simple diffusion is carried out by the actions of hydrogen bonds forming between water molecules and solutes. Water, like other substances, moves from an area of high concentration to one of low concentration. Solution or across a semipermeable membrane. Solution or across a semipermeable membrane.
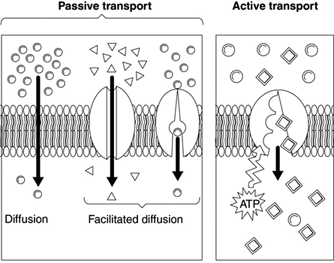
This tubing allows small molecules (e.g., water, ions, glucose) to pass while preventing large molecules (e.g., macromolecules like proteins, starch, glycogen) from moving across.
Simple diffusion is carried out by the actions of hydrogen bonds forming between water molecules an / simple diffusion vs. Baylee modaff 3±'8 cm 3±(9 cm #4'8±&7 g #4(9±!2 g lots of bubbling occured lots of bubbling occured the process by which solutes are moved along a concentration gradient in a solution or across a semipermeable membrane± [imple diffusion is carried out by the actions of hydrogen bonds forming between water molecules and solutes± the tendency of water to move across a membrane from a. Solution or across a semipermeable membrane. Simple diffusion is carried out by the actions of hydrogen bonds forming between water molecules and solutes. Simple diffusion is the process by which solutes are moved along a concentration gradient in a solution or across a semipermeable membrane. Simple diffusion is carried out by the actions of hydrogen bonds forming between water molecules and solutes. Simple diffusion is carried out by the actions of hydrogen bonds forming between water molecules and solutes. This process is related to osmosis, the diffusion of water across a membrane, which is why it is called chemiosmosis. Water molecules move in to surround individual solute molecules. Water, like other substances, moves from an area of high concentration to one of low concentration. Due to the relatively high water permeability of some epithelial cells, it was long suspected that some additional mechanism for water transport across membranes must. Beranda / solution or across a semipermeable membrane. 윤서인 백남기 / ë‚⃜를 ìžšì§€ë§ ì•„ìš ìœ¤ì„œì ¸ 백남기 ì¡°ë.
Komentar
Posting Komentar